The use of the pressure regulator in LPG systems for the automotive sector
 The use of LPG or methane gas to power cars is increasingly growing in the global automotive market thanks to both a reduction in costs and an eco-sustainable vision of the transport sector. Focusing on LPG, consumption compared to a classic petrol engine is about 20% higher but the advantage lies in the cost of this type of fuel which is about half.
The use of LPG or methane gas to power cars is increasingly growing in the global automotive market thanks to both a reduction in costs and an eco-sustainable vision of the transport sector. Focusing on LPG, consumption compared to a classic petrol engine is about 20% higher but the advantage lies in the cost of this type of fuel which is about half.As for the construction, there is both the possibility of converting gasoline cars to a hybrid system and the possibility of buying cars equipped with both systems. In addition, more and more performing engines are being developed that have all the necessary devices to ensure that they are used safely. Furthermore, according to the law, it is necessary that there is a switch that allows you to choose the type of power supply comfortably from the driving position.
How does an LPG system for the automobile sector work?
The system consists of various parts necessary for proper operation. In particular, we can note:- The tank: it is generally made of very resistant material to be able to withstand shocks or damage while preserving the health of the driver in case of an accident. The LPG inside is kept at a decidedly high pressure, equal to about 300 test bars and 220 operating bars and is in the liquid state. These pressures make it possible to store large quantities and effectively, allowing long journeys.
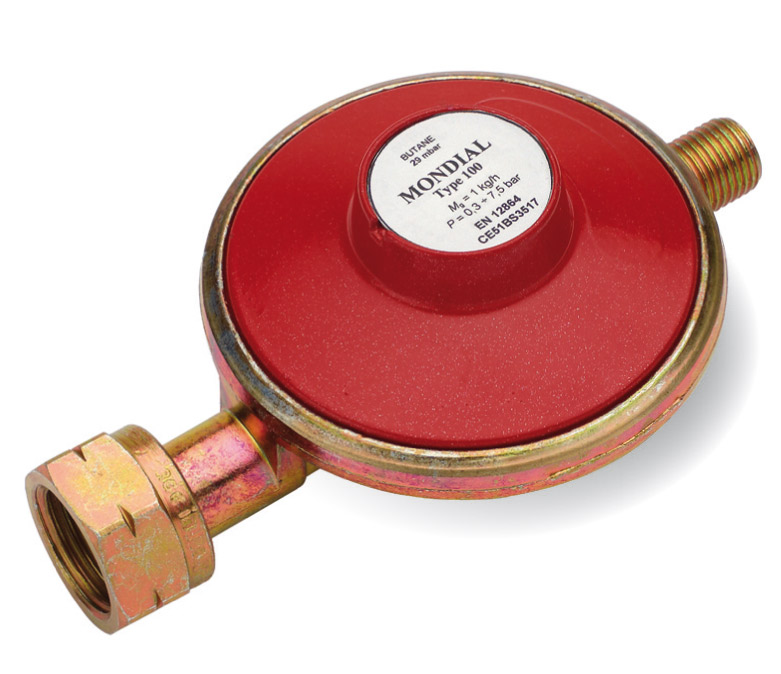
- Primary pressure reducer or regulator: used to bring the gas to the desired pressure for operation, always remaining in the liquid state. It goes from about 3/10 kg/cm2 to 0,4/1,2 kg/cm2.
- Vaporizer: the fluid enters a counter-current coil with hot water coming from the engine, causing a heating and vaporization of the LPG.
- Secondary pressure reducer or regulator: the pressure is brought back to a lower value than atmospheric pressure. It is essential that it works correctly to regulate flow to the carburetor. In addition, it is very sensitive to temperatures and operating conditions and must ensure that the pressure is always lower than the atmospheric one to prevent LPG from escaping freely into the atmosphere during the operation of the system.
- Intake manifold: through the injectors it reaches this component and a mixture with air suitable for combustion is formed.
- Combustion: at this point it is possible to cause combustion by making sure that the car is properly fueled.
From this simple schematic of the system it is clear that LPG certainly needs regulators or pressure reducers to properly perform its task within the power cycle of a car. Installation, maintenance and correct use are fundamental practices to prevent damage to components and that there is optimal operation.
21/12/2020
I contenuti di questo sito non hanno carattere di periodicità e non rappresentano 'prodotto editoriale'.