Electrical resistances for heating water
Electrical resistances for heating water when electricity is the only possible source
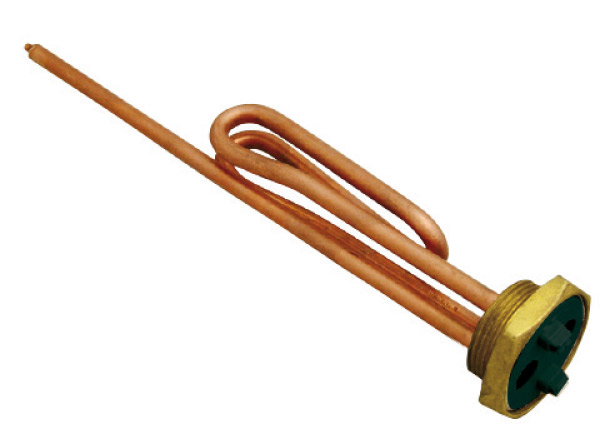

In plumbing systems, many times, it is not possible to use burners or flames to allow the conveyed water to be heated. This prohibition derives from legislative reasons but, above all, from regulations that aim to regulate the health and safety of all the people who live or may be in the vicinity of these systems.
Based on this premise, the need to heat the water for civil or domestic use with different methodologies appears evident: in particular, the most widespread is based on the use of devices such as electric resistances.
Based on this premise, the need to heat the water for civil or domestic use with different methodologies appears evident: in particular, the most widespread is based on the use of devices such as electric resistances.
What are electric resistances for water heating and how do they work?
Electric resistances, or also called resistors, are fundamental components in the world of electrical engineering and take their name from an important quantity of this branch of physics. In fact, electrical resistance is defined as “a scalar physical quantity that measures the tendency of a body to oppose the passage of current”. Within this definition there are some important concepts:
- Scalar: that is, not vector and not characterized by a direction;
- Opposite: the passage of a current inside a resistor will cause a voltage drop;
In fact, the main rules governing electrical resistances are the two laws of Ohm and the Joule effect. In particular, the first two determine the relationships between voltage, resistance and current, in addition to defining a methodology for calculating the resistance itself, while the last effect is fundamental for heating the water inside a circuit equipped with such components.
- Scalar: that is, not vector and not characterized by a direction;
- Opposite: the passage of a current inside a resistor will cause a voltage drop;
In fact, the main rules governing electrical resistances are the two laws of Ohm and the Joule effect. In particular, the first two determine the relationships between voltage, resistance and current, in addition to defining a methodology for calculating the resistance itself, while the last effect is fundamental for heating the water inside a circuit equipped with such components.
The joule effect at the base of the electrical resistances
Although the topic is of considerable complexity, at the base it presents the famous First Principle of Thermodynamics which, compared to the specific case, indicates that the electrical energy present inside a circuit does not disperse when passing through a resistor but is transformed into another form of energy, namely heat.
The effect, whose name derives from the surname of the physicist who first theorized it, can be easily explained by saying that the heat, or the thermal energy generated, is equal to the product between the square of the current and the value of the resistance. This has implications:
1. If the current flowing through a circuit doubles, or is halved, with the same resistance, the energy generated will be respectively equal to four times or a quarter of that obtained with the initial current value;
2. On the other hand, this increase, or decrease, cannot be obtained with an increase in resistance.
This effect has become increasingly important in the modern world with the expansion of electricity and is the basis of numerous appliances and devices with which we are in contact in everyday life: just think of any hairdryer or, referring precisely to the water, to any electric kettle.
The effect, whose name derives from the surname of the physicist who first theorized it, can be easily explained by saying that the heat, or the thermal energy generated, is equal to the product between the square of the current and the value of the resistance. This has implications:
1. If the current flowing through a circuit doubles, or is halved, with the same resistance, the energy generated will be respectively equal to four times or a quarter of that obtained with the initial current value;
2. On the other hand, this increase, or decrease, cannot be obtained with an increase in resistance.
This effect has become increasingly important in the modern world with the expansion of electricity and is the basis of numerous appliances and devices with which we are in contact in everyday life: just think of any hairdryer or, referring precisely to the water, to any electric kettle.
The concept of resistance in direct current and alternating current
Current can occur in two main forms: alternating and direct. What are the main differences?
- The alternating current is characterized by a sinusoidal trend and has advantages of both accumulation and production, allowing transport over long distances with benefits from an economic point of view.
- Direct current, on the other hand, is characterized by a constant trend due to the flow of electrical charges inside the conductor. It can be transported for very long distances by cables and is the energy supplied by the batteries. The main problem, however, is accumulation.
Alternating electricity is the widespread type nowadays all over the world thanks to its economic and practical convenience: in Europe three-phase alternating current with a frequency of 50 Hz is used. Also the electric resistances for the water are crossed by this type of current which is hampered not only by the resistance but also by the reactance X, which is a contribution deriving from the inductance I and the electric capacity C. In particular, the formula of the impedance Z is:
- The alternating current is characterized by a sinusoidal trend and has advantages of both accumulation and production, allowing transport over long distances with benefits from an economic point of view.
- Direct current, on the other hand, is characterized by a constant trend due to the flow of electrical charges inside the conductor. It can be transported for very long distances by cables and is the energy supplied by the batteries. The main problem, however, is accumulation.
Alternating electricity is the widespread type nowadays all over the world thanks to its economic and practical convenience: in Europe three-phase alternating current with a frequency of 50 Hz is used. Also the electric resistances for the water are crossed by this type of current which is hampered not only by the resistance but also by the reactance X, which is a contribution deriving from the inductance I and the electric capacity C. In particular, the formula of the impedance Z is:
Z=R+jX
where R is the resistance, X is the reactance and j indicates the imaginary part of the impedance.
Therefore, even the related calculations to derive the current intensity and the potential drop are more complicated when entering the world of complex numbers. The in-depth knowledge of these physical quantities represents a fundamental requirement for the realization of qualitatively suitable products.
Therefore, even the related calculations to derive the current intensity and the potential drop are more complicated when entering the world of complex numbers. The in-depth knowledge of these physical quantities represents a fundamental requirement for the realization of qualitatively suitable products.
08/04/2022
I contenuti di questo sito non hanno carattere di periodicità e non rappresentano 'prodotto editoriale'.